Composition (Figure 44)
· CodeItem – CodeItem class represents the named elements determined by the programming
language.
· Module – The Module class is a generic modeling element that represents an entire software
module or a component, as determined by the programming language and the software
development environment. A module is a discrete and identifiable program unit that
contains other program elements and may be used as a logical component of the software
system. Usually modules promote encapsulation (i.e., information hiding) through a
separation between the interface and the implementation. In the context of representing
existing software systems, modules provide the context for establishing the associations
between the programming language elements that are owned by them, especially when the
same logical component of a software product line is compiled multiple times with different
compilation options and linked into multiple executables. Instances of the Module class
represent the logical containers for program elements determined by the programming
language.
· PackageUnit – The PackageUnit class is a subtype for Module that logical collections of
program elements, as directly supported by some programming languages, such as Java.
· ClassUnit – The ClassUnit is an element that represents user-defined classes in objectoriented
languages.
· Datatype – Datatype class represents the named elements determined by the programming
language that describes datatypes.
· LanguageUnit – LanguageUnit is a logical container that owns definitions of primitive and
predefined datatypes for a particular language, as well as other common elements for a particular
programming language.
· MethodUnit – The MethodUnit represents member functions owned by a ClassUnit.
· CallableUnit – The CallableUnit represents a basic stand-alone element that can be called, such as a
procedure or a function.
· DataElement – The DataElement class is a generic element that defines the common properties of
several concrete classes that represent the named data items of existing software systems (for
example, global and local variables, record files, and formal parameters).
· ParameterUnit – ParameterUnit class is a concrete subclass of the DataElement class that represents
a formal parameter; for example, a formal parameter of a procedure.
· StorableUnit – StorableUnit represents a variable of existing software system – a computational
object to which different values of the same datatype can be associated at different times. From the
runtime perspective, a StorableUnit element represents a single computational object, which is
identified either directly (by name) or indirectly (by reference). StorableUnit represents both global
and local variables.
· ComputationalObject – ComputationalObject class represents the named elements determined by
the programming language, which describe certain computational objects at the runtime, for
example, procedures, and variables.
· PrimitiveType – The PrimitiveType is a generic element that represents primitive data types
determined by various programming languages.
· Screen – The Screen is a compound unit of display, such as a Web page or character-mode terminal
that is used to present capture information.
· Report – The Report is a compound unit of display, such as a printed report, that is used to present
information.
· UIDisplay – The UIDisplay is the superclass of Screen and Report. It represents a compound unit of
display.
· UIControl – The UIControl is a graphical control (text boxes, combo boxes, panel, menu…).
· UIEvent – The UIEvent class is an element representing events provided by a UIControl.
· FrameworkUnit – FrameworkUnit is a logical container that owns definitions of primitive
and predefined datatypes for a given framework, which may be either off-the-shelf
(distributed as a black-box component) or proprietary (source files may then be provided).
· ParameterKind – ParameterKind datatype defines the kind of parameter passing conventions.
· StorableKind – StorableKind enumeration data type defines several common properties of a
StorableUnit related to their life-cycle, visibility, and memory type.
· VisibilityKind – VisibilityKind enumeration data type defines several common properties of
a CodeItem related to its visibility.
· RecordType –
· EnumeratedType –
· UIField – UIField class is a concrete subclass of the DataElement class, and represents a
graphical component. It can be composed by a set of UIField, for a window by example.
· MemberUnit – MemberUnit class is a concrete subclass of the DataElement class that
represents a member of a class type.
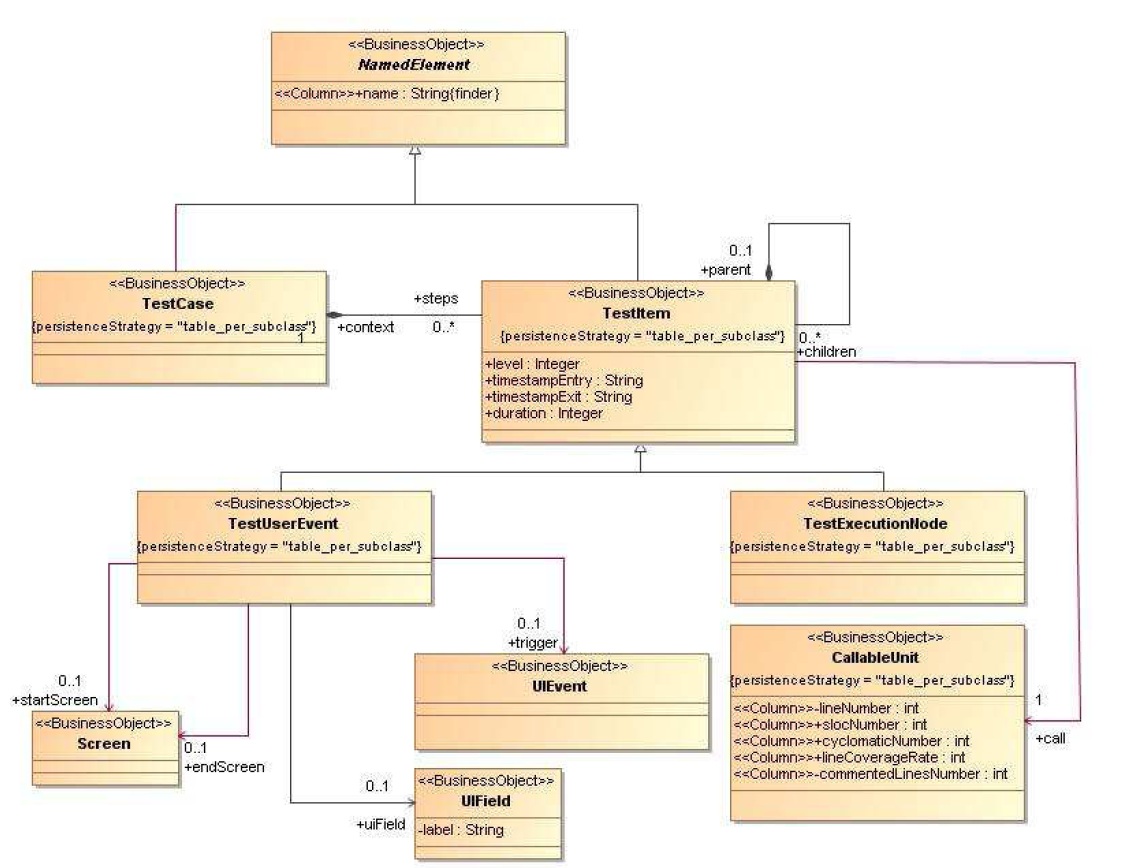 Figure 45 : TestArchitectureDiagram Diagram
Figure 45 : TestArchitectureDiagram Diagram
Page suivante : 7.2.3 Test Architecture
Retour au menu : Stratégie de test au sein du processus d’évolution d’architecture de Sodifrance
